The Basics of Essay Formatting

Essay formatting refers to the visual presentation of your paper, how it looks on the page. This includes page setup (margins, fonts, spacing), document structure (title, paragraphs, sections), and citation style (how you credit sources).
Why formatting matters
1. Demonstrates professionalism. Proper formatting signals you understand academic conventions and can follow instructions, critical in any academic or professional context.
2. Ensures readability. Consistent formatting creates a visual structure that makes your work easier to read and evaluate.
3. Prevents plagiarism. Correct citation formatting gives proper credit to sources while allowing readers to verify your research.
Formatting mistakes make professors question your attention to detail, even when your content is excellent. Missing page numbers, wrong margins, or inconsistent spacing suggest carelessness that costs points.
Need Perfectly Formatted Essays from Experts?
Perfect margins, citations, and structure, done right the first time
- Get essays formatted accurately in MLA, APA, or Chicago style
- Avoid costly formatting mistakes that lower grades
- Receive properly structured, submission ready documents
- Save time while ensuring academic compliance
Stop losing marks over formatting, let our essay writing service deliver polished, professor-approved papers.
Order NowStandard Essay Page Setup Requirements
These formatting elements remain consistent across most academic essays, regardless of which citation style you're using:
1. Margins
Standard: 1 inch on all sides (top, bottom, left, right)
This is universal across most academic formats. Don't try stretching margins to 1.25 inches to make essays appear longer, or shrinking to 0.75 inches to fit content; professors notice immediately.
Exception: Some specialized formats use different margins. Always check assignment requirements.
2. Font Choices
Standard: Times New Roman, 12 point
Other acceptable serif fonts include Georgia, Garamond, or Cambria. Some instructors accept sans-serif fonts like Arial or Calibri (11 to 12 point), but serif fonts remain the academic standard.
Never use:
- Decorative fonts (Comic Sans, Papyrus)
- Script or handwriting fonts
- Novelty or display fonts
- Font sizes under 11 or over 12 point
Creativity belongs in your arguments, not your font choices.
3. Spacing
Standard: Double space throughout the entire document
This includes your main text, quotations, notes, and reference lists. Double spacing provides room for instructor comments and improves readability.
Never:
- Single space to fit more content on fewer pages
- Add extra line breaks between paragraphs
- Use 1.5 spacing (it's either single or double)
- Mix spacing throughout your document
4. Alignment and Indentation
- Alignment: Left align your text with a ragged right edge. Don't use full justification; it creates uneven word spacing that reduces readability.
- Paragraph indentation: Indent the first line of each paragraph 0.5 inches (one Tab key press). Never add extra line breaks between paragraphs in academic essays.
5. Page Numbers
Include page numbers on every page (placement depends on citation style). Page numbers help instructors reference specific sections and ensure pages stay in order.
Common placements:
- Upper right corner
- Upper right with your last name
- Centered at bottom
Check your citation style guide for specific requirements.
Essays Structure Essentials
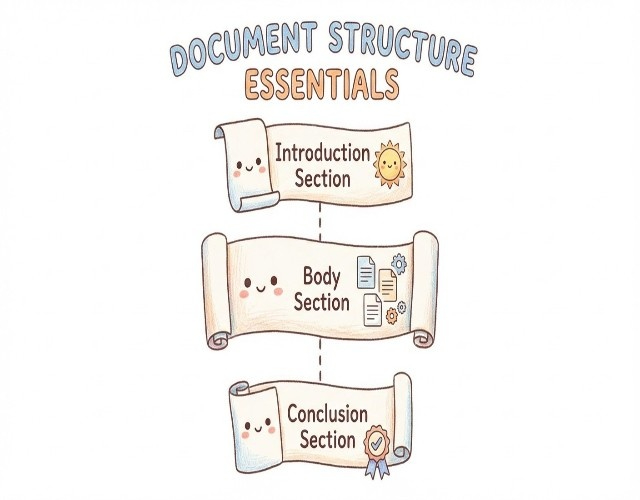
Academic essays follow a consistent three part structure:
A. Introduction Section
Establishes context for your topic, presents your thesis statement (main argument), and previews how you'll develop your ideas.
Length: Typically 10 to 15% of total essay length
For strategies on writing introductions that immediately establish credibility, see our guide on how to start an essay with college level techniques.
B. Body Section
Develops your argument through organized paragraphs. Each paragraph presents one main point supporting your thesis, backed by evidence and analysis.
Structure: 4 to 8 paragraphs typically (varies by essay length and complexity)
Strong topic sentences guide readers through your argument. Our guide on what is a topic sentence explains how to write clear signposts that maintain logical flow.
Smooth transitions show how ideas connect. See our comprehensive guide to transition words for essays with 300+ academic transitions organized by function.
C. Conclusion Section
Synthesizes your key insights, reinforces your thesis in light of the evidence presented, and explores broader implications.
Length: Typically 10 to 15% of total essay length
For proven conclusion strategies, check our guide on how to write a conclusion with techniques for creating resonant endings.
Essays Title Requirements
Your essay needs an effective title that previews your topic and signals your analytical approach.
Generic titles waste opportunities
- "Essay About Climate Change."
- "Research Paper."
- "English Assignment."
Effective titles signal sophistication
- "Economic Incentives vs. Moral Imperatives: Why Carbon Pricing Fails".
- "Digital Activism and Political Polarization in Social Media."
- "Narrative Structure and Unreliable Narration in The Great Gatsby."
For formulas and examples showing how to craft strong academic titles, see our complete guide on how to title an essay.
Choosing Your Citation Style for Essays
Most college essays require one of three citation styles. Each has specific rules for formatting, citations, and reference lists.
The Three Major Academic Formats
1, MLA Format (Modern Language Association)
- Used for: Humanities, English, literature, philosophy, languages, arts
- Key feature: Author-page intext citations emphasizing textual precision
- Example citation: (Hemingway 45)
- Why: Emphasizes WHO wrote it and WHERE to find it in the text
2. APA Format (American Psychological Association)
- Used for: Social sciences, psychology, sociology, education, business, nursing
- Key feature: Author date in text citations emphasizing research currency
- Example citation: (Johnson, 2024, p. 45)
- Why: Emphasizes WHO wrote it and WHEN (recency matters in empirical research)
- Used for: History, some humanities, graduate level work, publishing
- Key feature: Footnotes/endnotes allowing extensive documentation
- Example citation: Superscript number¹ linking to note
- Why: Keeps citations out of text flow while providing detailed documentation
Understanding Which Formatting Style to Use
Step 1: Check your assignment instructions. Most professors specify trequired format.
Step 2: Check your syllabus. Many instructors list preferred citation styles for all course assignments.
Step 3: Consider your discipline:
- English/Literature course? Probably MLA
- Psychology/Sociology course? Probably APA
- History course? Probably Chicago
Step 4: When in doubt, ASK. Don't assume. Using the wrong citation style costs points even if your writing is excellent.
Formatting Different Essay Components
Certain elements require specific formatting regardless of citation style:
1. Quotations
Short quotations (fewer than 4 lines): Integrate into your paragraph with quotation marks. Place citation after closing quotation mark, before period.
Long quotations (4+ lines): Format as block quotations, indent 0.5 inches from left margin, no quotation marks, double spaced. Introduce with a complete sentence ending in a colon.
2. Headings and Subheadings
Most standard essays use minimal headings. When required:
- Make headings descriptive, not generic
- Use consistent formatting throughout
- Follow your citation style's heading hierarchy
- Never use more heading levels than necessary
3. Lists
Academic essays rarely use bullet points or numbered lists. When necessary, integrate list information into paragraph text using transitional language.
Instead of a vertical list: The study identified:
- Economic factors
- Social factors
- Political factors
Write as a sentence: The study identified three key factors: economic instability, social fragmentation, and political polarization.
4. Tables and Figures
Tables: Place above or below relevant text. Include the table number and descriptive title above the table. Cite the source if using external data.
Figures: Place near relevant discussion. Include the figure number and caption below the figure.
Number both consecutively throughout your essay (Table 1, Table 2... Figure 1, Figure 2...).
Turn Formatting Confusion into Flawless Essays
Professional essay formatting support for stress free submissions
- Expert formatting aligned with university guidelines
- Correct citations, spacing, fonts, and headings
- Edited and reviewed for consistency and accuracy
- Suitable for essays, research papers, and assignments
When formatting feels overwhelming, our essay writing experts are just a click away.
Order NowFormatting by Essay Length

Different essay lengths require different formatting approaches:
Short Essays (500 to 1000 words)
Typically 2 to 4 pages double spaced. May not require a separate title page depending on citation style. Focus on tight structure and efficient argumentation.
Our 500 word essay guide shows formatting requirements for shorter assignments, while the 1000 word essay guide covers mid-length papers with research expectations.
Medium Essays (1500 to 2500 words)
Standard college essay length. Requires full formatting compliance, including proper citations, an organized structure, and a polished presentation. Most assignments fall into this range.
Long Essays (3000+ words)
Research papers require extensive documentation. May include headings, multiple sections, tables/figures, and appendices. Need a strong organizational structure to maintain readability.
Digital Submission and File Formatting of Essays
Most college assignments are submitted electronically. Follow these guidelines:
1. File Naming
Use descriptive names, including your information and assignment details:
- Correct: Smith_ENG101_Essay1_Analysis.docx
- Incorrect: Essay.docx
- Incorrect: FinalDraft.docx
Professors download dozens of files, make yours identifiable.
2. File Format
- Preferred: .docx (Microsoft Word) for most assignments. Preserves formatting and allows instructor comments.
- Alternative: PDF when requested or when you want guaranteed formatting consistency across devices.
- Avoid: .pages (Mac-only), .odt (OpenOffice), or .rtf unless specifically requested.
3. Final Formatting Check
Before submitting:
- Open your document on a different device to verify formatting stayed consistent
- Check that page numbers appear correctly
- Verify citations match your reference list
- Confirm margins, spacing, and font meet requirements
- Run spell check one final time
- Read the essay aloud, catching errors missed during silent reading
Formatting mistakes can undermine strong content. To avoid last minute formatting issues, consider a professional essay writing service that reviews margins, spacing, citations, and structure before submission.
Common Essay Formatting Mistakes That Cost Points
Even strong essays lose points for these preventable errors:
1. Mixing Citation Styles
Using MLA in text citations with APA style references, or mixing elements from different styles throughout. This signals you don't understand academic conventions.
Fix: Choose ONE style at the beginning. Apply it consistently throughout. Never mix.
2. Incorrect Spacing
Single spacing to fit more content, adding extra line breaks between paragraphs, or inconsistent spacing throughout.
Fix: Double space everywhere. No exceptions unless your specific citation style allows them in particular sections (like Chicago footnotes).
3. Wrong Margins
Stretching margins to 1.25 or 1.5 inches to make essays appear longer, or shrinking to 0.75 inches to fit content.
Fix: Stick to 1 inch margins exactly. Professors notice margin manipulation immediately.
4. Improper Indentation
Failing to indent paragraph first lines, manually spacing with the spacebar instead of the Tab key, or inconsistent indentation.
Fix: First line of every paragraph should be indented 0.5 inches using the Tab key. Every paragraph. No exceptions.
5. Font Issues
Using Comic Sans, decorative fonts, or non standard sizes to "stand out."
Fix: Times New Roman 12 point unless instructed otherwise. Let your arguments stand out, not your fonts.
6. Missing Page Numbers
Forgetting page numbers entirely, placing them incorrectly, or using the wrong format.
Fix: Verify page numbering appears consistently where your citation style requires it.
7. Citation Errors
Incorrect in text format, missing citations for paraphrased material, improperly formatted reference entries, or forgetting hanging indentation.
Fix: Every source cited in text must appear in your reference list, and vice versa. Check your citation style guide for exact formatting.
Understanding writing conventions beyond just formatting, grammar rules, punctuation standards, and capitalization guidelines ensures your essays look professional throughout.
Get Your Essay Formatted the Right Way
Because great content deserves professional presentation
- Customized formatting based on your instructor’s requirements
- Error free citations and references
- Clean, professional layout that boosts readability
- Fast turnaround with reliable academic support
Submit with confidence, choose our essay writing service for flawless formatting and better grades.
Order NowReady to Format Essays Perfectly?
You now understand the formatting fundamentals that apply across academic writing: standard page setup with 1 inch margins and double spacing, proper document structure with introduction, body, and conclusion, appropriate font choices and paragraph formatting, which citation style to use based on your discipline, and where to find complete guides for each citation system.
Formatting isn't optional; it demonstrates professionalism, ensures readability, and signals you understand academic conventions. Taking time to format correctly protects your grade and prepares you for professional contexts where presentation matters.
For comprehensive coverage of essay writing fundamentals beyond formatting, explore our complete essay writing guide with detailed sections on thesis development, research strategies, and revision techniques.








-20154.jpg)