Quick Comparison Table: APA vs MLA
Feature | APA Format | MLA Format |
In-text citation | (Smith, 2024) | (Smith 45) |
With page number | (Smith, 2024, p. 45) | (Smith 45) |
Emphasis | Publication date | Page location |
Final list name | References | Works Cited |
Best for | Sciences, social sciences | Humanities, literature |
Date format | 2024, March 15 | 15 March 2024 |
Title page | Required separate page | No separate page |
Running head | Page numbers only (students) | Last name + page number |
When to Use MLA vs APA
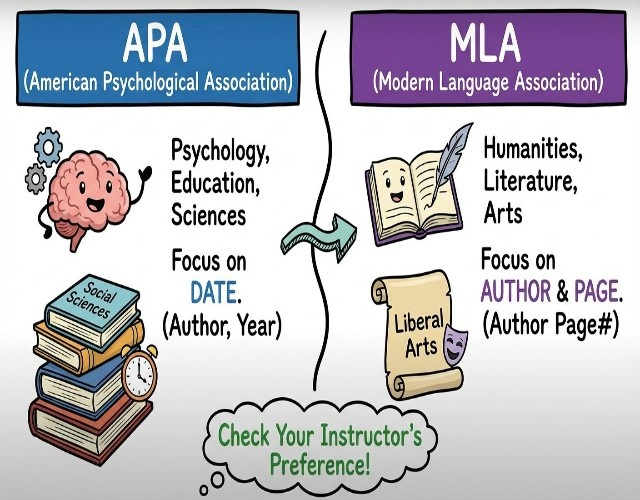
Use APA Format When:
Your field is:
- Psychology
- Education
- Nursing
- Sociology
- Business
- Any social science
Your assignment emphasizes:
- Recent research and publication dates
- Empirical studies and data
- Scientific methodology
- Current trends and findings
Your professor says:
- "Use APA format"
- "Follow the Publication Manual."
- "Use author-date citations."
Need to learn more about APA formatting? Follow our APA Format guide.
Use MLA Format When:
Your field is:
- Literature
- Languages
- Film studies
- Cultural studies
- Creative writing
- Any humanities subject
Your assignment emphasizes:
- Textual analysis
- Close reading
- Specific passages and quotes
- Literary interpretation
Your professor says:
- "Use MLA format"
- "Follow the MLA Handbook."
- "Use parenthetical citations."
For a deeper understanding of MLA formatting, see our MLA Format guide.
SWITCHING BETWEEN APA AND MLA?
Complete Papers Written, Researched, and Cited According to Your Exact Style Requirements
- Submit your topic and citation style requirements
- We adapt to any citation style instantly
- No confusion, no mistakes
- Perfect formatting guaranteed
Stop stressing about citation switches.
Order NowAPA Vs MLA In-Text Citation Differences
Basic Citation Format
APA:
- Emphasizes WHEN research was published
- Always includes year
- Uses a comma between author and year
- Format: (Author, Year) or (Author, Year, p. Page)
Examples:
Recent research supports this claim (Johnson, 2024).
Johnson (2024) supports this claim.
The study found "significant results" (Johnson, 2024, p. 67).
MLA:
- Emphasizes WHERE in the source you found information
- Never includes year in citation
- No punctuation between author and page
- Format: (Author Page) with NO comma
Examples:
Recent research supports this claim (Johnson 67).
Johnson supports this claim (67).
The study found "significant results" (Johnson 67).
Multiple Authors
| APA (two authors): (Smith & Jones, 2024) Smith and Jones (2024) found... |
| MLA (two authors): (Smith and Jones 67) Smith and Jones found... (67). |
| APA (three or more): (Martinez et al., 2024) Use "et al." from the first citation |
| MLA (three or more): (Martinez et al. 67) Use "et al." from the first citation |
Direct Quotes
APA:
- Always use "p." or "pp." before page numbers
- Short quotes: "Quote text" (Author, Year, p. #).
- Long quotes (40+ words): Block indent, citation after period
Example:
The research confirms "significant cognitive improvements" (Chen, 2024, p. 156).
MLA:
- NEVER use "p." or "pp." before page numbers
- Short quotes: "Quote text" (Author #).
- Long quotes (4+ lines prose): Block indent, citation after period
Example:
The research confirms "significant cognitive improvements" (Chen 156).
Basic MLA vs APA Citation Structure
The most visible difference between APA and MLA appears in parenthetical citations. APA requires both publication year and page number: (Smith, 2023, p. 45). MLA requires only the page number: (Smith 45). This reflects APA's focus on research currency, as opposed to MLA's focus on textual analysis.
- APA in-text citation: Recent research confirms this trend (Martinez, 2024, p. 78).
- MLA in-text citation: Literary critics have noted this pattern (Martinez 78).
When the author's name appears in your sentence, APA still requires the year immediately after the name, while MLA places only the page number at the end of the sentence.
- APA with author in text: Martinez (2024) argues that climate patterns have shifted significantly (p. 78).
- MLA with author in text: Martinez argues that climate patterns have shifted significantly (78).
Multiple Authors
APA and MLA handle multiple authors differently in both citations and reference lists. APA uses an ampersand (&) between authors, while MLA uses "and." For three or more authors, APA uses "et al." after the first author, while MLA also uses "et al." but formats it differently.
- Two authors - APA: (Smith & Johnson, 2023, p. 45)
- Two authors - MLA: (Smith and Johnson 45)
- Three or more authors (APA): (Martinez et al., 2024, p. 112)
- Three or more authors (MLA): (Martinez et al. 112)
Direct Quotations
Both styles require page numbers for direct quotes, but formatting differs. APA uses "p." for single pages and "pp." for page ranges. MLA uses no prefix, just the page numbers.
- Short quote - APA: As one researcher notes, "Climate change affects biodiversity" (Chen, 2023, p. 89).
- Short quote - MLA: As one researcher notes, "Climate change affects biodiversity" (Chen 89).
- Quote with page range - APA: The study revealed "significant correlations between variables" (Davis, 2024, pp. 45-47).
- Quote with page range - MLA: The study revealed "significant correlations between variables" (Davis 45-47).
No Author Citations
When sources lack identified authors, APA uses shortened titles in quotation marks for articles or italics for books. MLA follows the same convention but with slightly different punctuation.
- No author - APA: The policy has been criticized ("New Guidelines," 2024, p. 3).
- No author - MLA: The policy has been criticized ("New Guidelines" 3).
Reference Page vs Works Cited
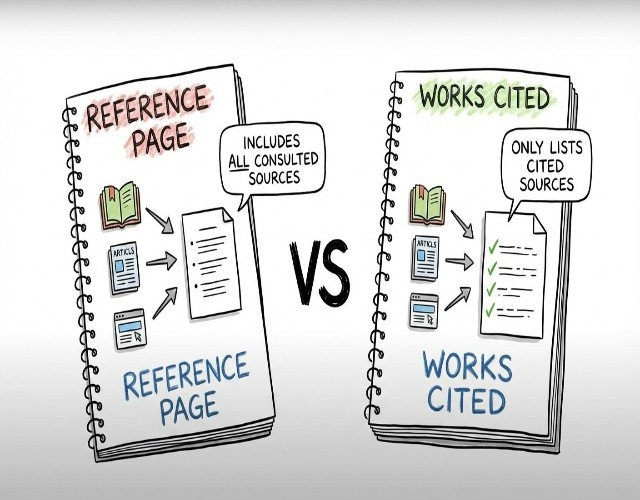
Page Title and Setup
APA References Page:
- Title: "References" (centered, bold)
- Starts on a new page after the paper
- Double-spaced throughout
- Hanging indent (0.5 inch)
- Alphabetized by author's last name
MLA Works Cited Page:
- Title: "Works Cited" (centered, not bold)
- Starts on a new page after the paper
- Double-spaced throughout
- Hanging indent (0.5 inch)
- Alphabetized by author's last name
Book Citation Format
APA:
Smith, J. M. (2024). Understanding cognitive psychology. Academic Press.
Key APA features:
- Author: Last name, Initials
- Year in parentheses after author
- Title in sentence case, italicized
- Publisher only (no location)
MLA:
Smith, Jennifer M. Understanding Cognitive Psychology. Academic Press, 2024.
Key MLA features:
- Author: Last name, Full first name
- Year at END of entry
- Title in Title Case, italicized
- Publisher, then year
Journal Article Format
APA:
Chen, L., & Martinez, P. (2024). Effects of sleep on memory. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 89(4), 412-428. https://doi.org/10.1080/12345678
Key APA features:
- Initials only
- Year after author
- Article title sentence case, no quotes
- Journal name Title Case, italicized
- Volume italicized, issue in parentheses
- DOI preferred
MLA:
Chen, Lisa, and Pablo Martinez. "Effects of Sleep on Memory." Journal of Cognitive Psychology, vol. 89, no. 4, 2024, pp. 412-28.
Key MLA features:
- Full first names
- Year near END
- Article title Title Case, in quotes
- Journal name Title Case, italicized
- "vol." and "no." spelled out
- "pp." before page numbers
Website Citation Format
APA:
Garcia, M. (2024, July 15). Understanding panic disorders. Mental Health Foundation. https://www.mentalhealthfoundation.org/panic
MLA:
Garcia, Michael. "Understanding Panic Disorders." Mental Health Foundation, 15 July 2024, www.mentalhealthfoundation.org/panic.
Key difference: APA uses Month Day, Year format; MLA uses Day Month Year format.
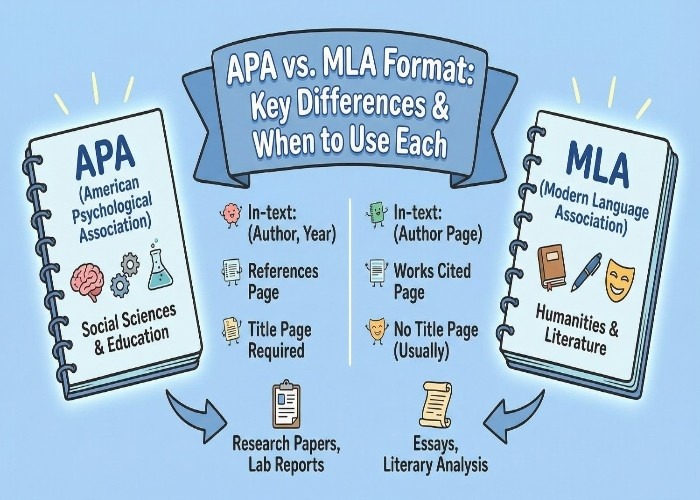
APA vs MLA Paper Formatting Differences
Title Page
APA:
- Requires SEPARATE title page (page 1)
- Title centered, bold, middle of page
- Your name below the title
- Institution, course, instructor, date
- No separate title page = immediate point deduction
MLA:
- NO separate title page
- Heading on page 1, top left:
- Your name
- Professor name
- Course name
- Date (Day Month Year)
- Title centered below heading
- Text starts immediately after the title
Headers
APA (student papers):
- Page number ONLY in top right corner
- Starts on title page (page 1)
- No running head for students
MLA:
- Last name + page number in top right
- Example: Martinez 1, Martinez 2
- Appears on EVERY page, including the first page
Spacing and Margins
Both styles:
- 1-inch margins on all sides
- Double-space everything
- 0.5-inch paragraph indent
No differences here: both require the same spacing.
Font Choices
APA 7th edition accepts:
- Times New Roman 12pt
- Calibri 11pt
- Arial 11pt
- Georgia 11pt
- Lucida Sans Unicode 10pt
MLA accepts:
- Any readable 12pt font
- Times New Roman most common
- Calibri, Arial acceptable
PERFECT CITATIONS IN ANY STYLE
Stop Worrying About Citation Mistakes: Get Flawlessly Formatted Papers
- Expert writers format every citation perfectly
- APA, MLA, Chicago, IEEE: we do them all
- Switch styles without thinking twice
- Zero formatting errors
Stop wrestling with style manuals.
Order NowTitle Capitalization Rules
APA Sentence Case (for article/book titles in References)
Capitalize:
- First word of title
- First word after colon
- Proper nouns
Example:
Understanding cognitive development in early childhood and adolescence
Do NOT capitalize: Articles, prepositions, conjunctions (unless first word)
MLA Title Case (for all titles)
Capitalize:
- First word
- Last word
- All major words (nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs)
Example:
Understanding Cognitive Development in Early Childhood and Adolescence
Do NOT capitalize: Articles (a, an, the), short prepositions (in, on, at, to), coordinating conjunctions (and, but, or), unless first or last word.
Common APA vs MLA Mistakes When Switching Styles
| Mistake | Incorrect Format | Correct Format | Fix / Rule |
|---|---|---|---|
| Using APA punctuation in MLA | Incorrect: (Smith, 45) Incorrect: (Smith, 2024) | Correct: (Smith 45) | MLA uses no punctuation between author and page number and does not include the year in in-text citations. |
| Using MLA punctuation in APA | Incorrect: (Smith 2024) Incorrect: (Smith 2024 45) | Correct: (Smith, 2024) Correct: (Smith, 2024, p. 45) | APA requires a comma after the author and “p.” before page numbers. |
| Wrong date format | Incorrect (APA): 15 March 2024 Incorrect (MLA): March 15, 2024 | Correct (APA): 2024, March 15 Correct (MLA): 15 March 2024 | APA uses Year, Month, Day; MLA uses Day, Month, Year. |
| Creating an MLA title page | Incorrect: Separate title page | Correct: Heading on page 1 | MLA does not require a separate title page unless specifically instructed. |
| Using initials in MLA | Incorrect: Smith, J. M. Book Title. | Correct: Smith, Jennifer M. Book Title. | MLA uses full first names, not initials. |
| Using “p.” in MLA citations | Incorrect: (Johnson, p. 45) Incorrect: (Johnson, p. 45) | Correct: (Johnson 45) | MLA never uses “p.” or “pp.” in in-text citations. |
| Wrong title case in APA references | Incorrect: Understanding Cognitive Development in Early Childhood | Correct: Understanding cognitive development in early childhood | APA uses sentence case for reference titles. |
| Missing MLA header | Incorrect: Page numbers only | Correct: Last name + page number | MLA requires the author’s last name and page number in the header. |
Converting Between APA and MLA
From APA to MLA
- In-text citations:
- Remove year: (Smith, 2024, p. 45) becomes (Smith 45)
- Remove commas: (Smith, 2024) becomes (Smith 45) if adding page number.
- Remove "p." or "pp.": (Smith, 2024, p. 45) becomes (Smith 45)
- References to Works Cited:
- Change page title from "References" to "Works Cited."
- Expand author initials to full names
- Move the year from after the author to the end of the entry
- Change title to Title Case
- Add "pp." before page numbers for articles
- Remove DOI (optional in MLA)
- Paper format:
- Remove title page, create MLA heading on page 1
- Add last name to page numbers
- Center title on page 1 (not bold)
From MLA to APA
- In-text citations:
- Add year: (Smith 45) becomes (Smith, 2024)
- Add a comma after the author: (Smith 45) becomes (Smith, 2024, p. 45)
- Add "p." before page: (Smith, 2024, p. 45)
- Works Cited to References:
- Change page title from "Works Cited" to "References."
- Shorten first names to initials
- Move year from end to after author (in parentheses)
- Change title to sentence case
- Remove "pp." from article pages
- Add DOI if available
- Paper format:
- Create a separate title page
- Remove last name from page numbers
- Remove MLA heading from page 1
APA or MLA Side by Side: Same Source, Both Styles
Book Citation
| Element | APA Style | MLA Style |
|---|---|---|
| In-text citation | (Morrison, 1987) | (Morrison 45) |
| Reference entry | Morrison, T. (1987). Beloved. Knopf. | Morrison, Toni. Beloved. Knopf, 1987. |
Journal Article
| Element | APA Style | MLA Style |
|---|---|---|
| In-text citation | (Chen & Rodriguez, 2024) | (Chen and Rodriguez 234) |
| Reference entry | Chen, M., & Rodriguez, L. (2024). Sleep and memory. Journal of Psychology, 89(3), 234–256. | Chen, Michael, and Lisa Rodriguez. “Sleep and Memory.” Journal of Psychology, vol. 89, no. 3, 2024, pp. 234–56. |
Website
| Element | APA Style | MLA Style |
|---|---|---|
| In-text citation | (American Psychological Association, 2024) | (American Psychological Association) |
| Reference entry | American Psychological Association. (2024, March 15). Mental health resources. https://www.apa.org/resources | American Psychological Association. “Mental Health Resources.” 15 Mar. 2024, www.apa.org/resources. |
Quick Decision Guide
Choose APA if:
- Professor specifically requires it
- You're in psychology, education, nursing, or social sciences
- Your paper discusses empirical research
- Publication dates matter to your argument
- You're citing mostly recent research (last 5-10 years)
Choose MLA if:
- Professor specifically requires it
- You're in literature, languages, or humanities
- Your paper analyzes texts closely
- You need specific page references
- You're quoting literary works frequently.
Still confused? Our professional essay writing service handles both styles perfectly; we switch between APA, MLA, Chicago, IEEE, and ASA seamlessly, formatting every citation exactly right.
Free Comparison Resources
APA vs MLA Quick Reference
APA and MLA Paper Format Templates
Citation Conversion Worksheet (APA and MLA Formats)
Side by Side APA and MLA Citation Examples
Need Perfect Citations in APA or MLA?
Podcasts, Social Media, Videos, Interviews, Get Every Non-Traditional Source Cited Correctly
- Specify any special citation challenges
- We master all styles flawlessly
- Switch between formats without errors
- Zero citation mistakes, guaranteed
Free revisions until you're 100% satisfied.
Order NowMaster Both APA & MLA Styles
Understanding the differences between APA and MLA comes down to recognizing their distinct priorities: APA emphasizes publication dates for scientific currency, while MLA emphasizes page locations for textual analysis. Once you understand this fundamental difference, the formatting rules make logical sense.
Most mistakes happen when switching styles mid-semester or applying one style's rules to the other. Use this comparison to identify which format your assignment requires, then follow that style's rules consistently. For deeper insight into different formats, explore our citation style guide for a complete overview.

-19434.jpg)
-19334.jpg)
-19329.jpg)

-19406.jpg)


