Cause and Effect Essay Block Structure Outline Template (Copy-Paste Ready)
Use the block method outline for independent causes and effects."
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Hook: [Striking statistic, question, or anecdote]
B. Background: [Brief context - 2-3 sentences]
C. Thesis Statement: [Specific cause] leads to [specific effects] because [brief reason]
II. BODY SECTION 1: CAUSES
A. Cause 1: [First major cause]
1. Evidence: [Statistic or expert quote]
2. Explanation: [How this functions as a cause]
3. Transition: [Connect to next cause]
B. Cause 2: [Second major cause]
1. Evidence: [Data or research finding]
2. Explanation: [Mechanism of causation]
3. Transition: [Connect to next cause]
C. Cause 3: [Third major cause]
1. Evidence: [Supporting source]
2. Explanation: [Why this matters]
3. Transition: [Bridge to effects section]
III. BODY SECTION 2: EFFECTS
A. Effect 1: [First major effect]
1. Evidence: [Statistic or case study]
2. Analysis: [Impact and significance]
3. Transition: [Connect to next effect]
B. Effect 2: [Second major effect]
1. Evidence: [Research data]
2. Analysis: [Consequences]
3. Transition: [Connect to next effect]
C. Effect 3: [Third major effect]
1. Evidence: [Supporting documentation]
2. Analysis: [Long-term implications]
3. Transition: [Lead to conclusion]
IV. CONCLUSION
A. Restate Thesis: [Rephrase main argument]
B. Summary: [Briefly recap key causes and effects]
C. Significance: [Why this relationship matters]
D. Final Thought: [Broader implications or call to action]Cause and Effect Essay Chain Structure Outline Template (Copy-Paste Ready)
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Hook: [Attention-grabbing opener]
B. Context: [Brief background - 2-3 sentences]
C. Thesis Statement: [Initial cause] triggers [sequential effects], ultimately resulting in [final outcome]
II. CAUSE-EFFECT PAIR 1
A. Initial Cause: [Starting event or condition]
1. Evidence: [Data supporting this cause]
2. Mechanism: [How it functions]
B. Effect 1: [Direct result of initial cause]
1. Evidence: [Proof of this effect]
2. Significance: [Why this outcome matters]
C. Transition: [How Effect 1 becomes Cause 2]
III. CAUSE-EFFECT PAIR 2
A. Cause 2 (Effect 1): [Previous effect now acting as cause]
1. Evidence: [Supporting data]
2. Connection: [Link to previous section]
B. Effect 2: [Result of Cause 2]
1. Evidence: [Research or statistics]
2. Analysis: [Impact of this effect]
C. Transition: [How Effect 2 becomes Cause 3]
IV. CAUSE-EFFECT PAIR 3
A. Cause 3 (Effect 2): [Second effect now causing new outcome]
1. Evidence: [Documentation]
2. Mechanism: [How causation works]
B. Effect 3: [Final major consequence]
1. Evidence: [Strong supporting data]
2. Analysis: [Cumulative impact]
C. Transition: [Lead to conclusion]
V. CONCLUSION
A. Restate Thesis: [Rephrase causal chain]
B. Summary: [Brief recap of sequential relationship]
C. Cumulative Impact: [Overall significance of chain]
D. Final Statement: [Closing thought or broader implications].?| Remember! Chain structure works best when effects become causes. |
NEED IT WRITTEN FOR YOU?
Our professional writers have helped thousands of students succeed
- Professional essay from your outline
- Properly structured and cited
- Delivered on deadline
- Unlimited revisions until you're satisfied
Hand us your outline, get back a polished essay.
Order NowCause and Effect Essay Structure Breakdown: Percentage Guidelines
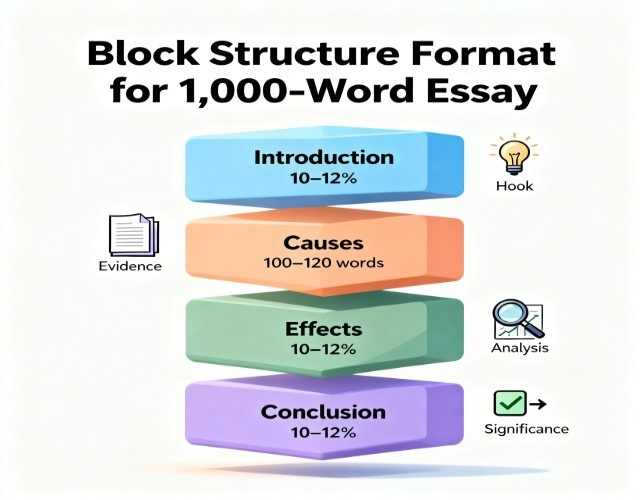
Format characteristics:
- Clear separation between causes and effects.
- Transition paragraph between sections (50-75 words).
- Each cause/effect gets equal development space.
- Parallel structure throughout sections.
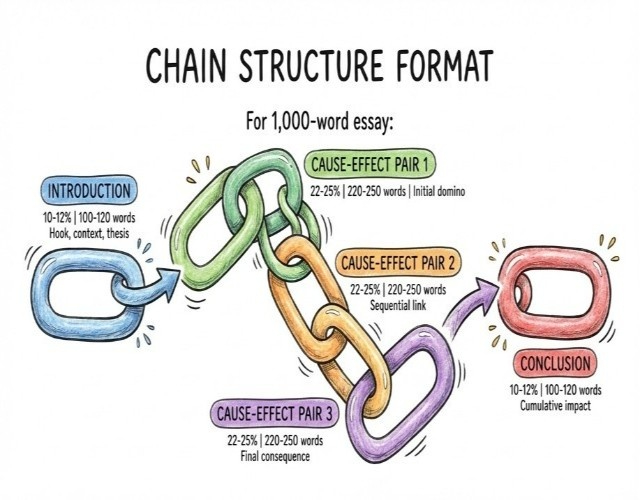
Format characteristics:
- Each pair shows a direct cause-and-effect relationship.
- Transition sentences connect pairs (1-2 sentences each).
- Progressive development showing accumulation.
- Emphasis on the sequential nature.
| Pro Tip: Selecting the right cause and effect essay topics makes it easier to structure each section of your essay outline. |
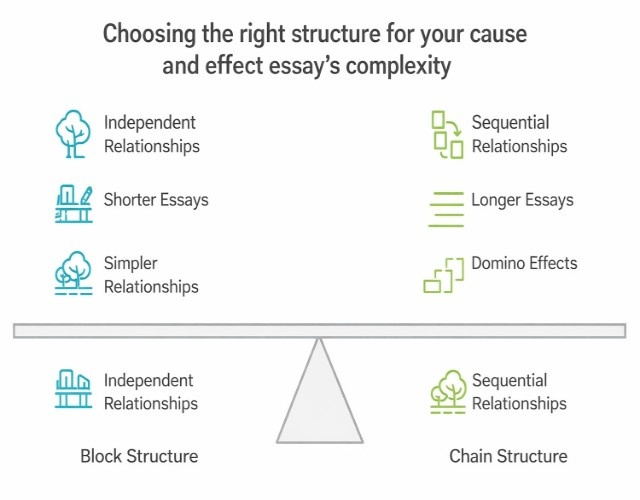
Framework Comparison (Block Vs Chain Structure)
Aspect | Block Structure | Chain Structure |
Organization | All causes, then all effects | Alternating cause-effect pairs |
Best For | Multiple independent causes/effects | Sequential causal chains |
Complexity | Simpler to organize | Shows direct connections |
Reader Experience | Easier to follow distinct sections | More dynamic, narrative flow |
Essay Length | Works for shorter essays | Better for longer analyses |
Typical Use | Cause-focused or effect-focused | Combined cause-and-effect |
Format Variations by Length
Choose the cause and effect essay format that matches your assignment length
Short Format (500-750 words)
Structure: Block or chain with 2 main points.
Introduction: 60-90 words
Body Point 1: 150-225 words
Body Point 2: 150-225 words
Conclusion: 60-90 wordsBest for:
- In-class essays.
- Quick assignments.
- Focused single-cause or single-effect analysis.
Template adjustment: Reduce to 2 causes or 2 effects instead of 3
Medium Format (1,000-1,500 words)
Structure: Block or chain with 3-4 main points.
Introduction: 120-180 words
Body Point 1: 250-300 words
Body Point 2: 250-300 words
Body Point 3: 250-300 words
[Optional Point 4: 250-300 words]
Conclusion: 120-180 wordsBest for:
- Standard college essays.
- Typical homework assignments.
- Balanced analysis with depth.
Long/Research Format (2,000-3,000 words)
Structure: Usually a block with 4-6 main points or an extended chain.
Introduction: 200-300 words
Body Point 1: 350-450 words
Body Point 2: 350-450 words
Body Point 3: 350-450 words
Body Point 4: 350-450 words
[Optional Points 5-6: 350-450 words each]
Conclusion: 200-300 wordsBest for:
- Research papers.
- Final projects.
- Comprehensive analysis requiring multiple sources.
Template adjustment:
- Expand each section with 2-3 pieces of evidence.
- Add subsections for complex points.
- Include counterarguments or alternative explanations.
Template adjustment: Use standard 3-point structure or expand to 4 points
| Following a clear cause and effect essay outline format helps students organize their ideas logically and ensures a smooth flow. |
TIGHT DEADLINE APPROACHING?
Professional writing assistance tailored to your needs
- Expert writers ready now
- Any length, any deadline
- Properly formatted and cited
- Satisfaction guaranteed or money back
Professional essays from outline to final draft.
Get Expert HelpCause and Effect Essay Paragraph Structure Template (PEEL Method)

Here's a complete outline for cause and effect essay assignments. Each body paragraph should follow this format:
[p] POINT - Topic sentence stating the cause or effect
Format: "One major cause of [phenomenon] is [specific factor]."
[E] EVIDENCE - Data, statistics, or expert testimony
Format: "According to [source], [statistic or finding]."
[E] EXPLANATION - How evidence proves your point
Format: "This demonstrates causation because [mechanism explanation]."
[L] LINK - Connect to thesis or transition to next paragraph
Format: "Beyond [current point], [next point] also contributes significantly."
Body Paragraph Template Structure
For Cause Paragraph:
[Topic Sentence] The primary cause of rising student debt is [specific cause].
[Evidence] According to the Federal Reserve, student loan debt reached
$1.7 trillion in 2024, with the average borrower owing
$37,000 (Federal Reserve, 2024).
[Explanation] This escalation stems directly from [mechanism: tuition increases
outpacing inflation, reduced state funding, expanded loan access without
income caps. When universities raised tuition by 180% between 2000-2024
While median household Income increased only 25%, so students had no
choice but to borrow more.
[Link] This financial burden creates immediate effects on graduates'
economic decisions.
For Effect Paragraph:
[Topic Sentence] One significant effect of student debt is delayed homeownership
among millennials.
[Evidence] Research from the Urban Institute shows that homeownership rates
for 30-year-olds dropped from 45% in 2000 to 37% in 2024, with student debt
cited as the primary factor (Urban Institute, 2024).
[Explanation] This delay occurs because monthly loan payments (averaging $400)
prevent debt-holders from saving for down payments while simultaneously
lowering credit scores, making mortgage approval more difficult.
Graduates must choose between loan payments and savings, inevitably
postponing major purchases.
[Link] This housing market impact creates broader economic consequences for
consumer spending.
Cause and Effect Essay Filled-In Outline (Chain Structure)
Note: This shows a filled outline structure, not a complete essay. For full essay samples, see our cause and effect essay examples page.
Topic: The Chain Effect of Sleep Deprivation on Student Performance
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Hook: 70% of college students report sleeping less than 7 hours nightly
B. Context: Sleep deprivation has become normalized in academic culture
C. Thesis: Chronic sleep deprivation triggers cognitive impairment, which
causes academic decline, ultimately resulting in increased dropout rates
II. CAUSE-EFFECT PAIR 1
A. Initial Cause: Students sleep less than 6 hours per night
Evidence: CDC data shows 65% of students average 5-6 hours
Mechanism: Academic pressure, part-time work, social commitments
B. Effect 1: Cognitive function declines (memory, focus, processing)
Evidence: Sleep studies show a 40% reduction in cognitive performance
Significance: Makes learning and retention difficult
Transition: This cognitive decline directly impacts academic work quality
III. CAUSE-EFFECT PAIR 2
A. Cause 2: Impaired cognitive function (Effect 1)
Evidence: Brain scans show reduced prefrontal cortex activity
Connection: Students cannot focus during lectures or study sessions
B. Effect 2: Academic performance drops (lower grades, missed assignments)
Evidence: GPA correlation studies show a 0.5-point average decline
Analysis: Students struggle despite effort, creating frustration
Transition: Poor academic performance creates psychological stress
IV. CAUSE-EFFECT PAIR 3
A. Cause 3: Academic failure combined with sleep deprivation (Effect 2)
Evidence: Mental health assessments show an anxiety spike
Mechanism: Stress hormones compound sleep problems
B. Effect 3: Increased dropout rates and degree non-completion
Evidence: Retention studies link sleep patterns to dropout (25% higher)
Analysis: Cumulative effect creates a cycle students can't break
Transition: This demonstrates how initial sleep choices cascade
V. CONCLUSION
A. Restate: Sleep deprivation initiates cognitive decline leading to academic
failure causing dropout risk.
B. Summary: Each effect amplifies the next, creating destructive cycle
C. Impact: Understanding this chain helps identify intervention points
D. Final: Addressing sleep could prevent downstream academic consequencesThis outline format shows structure only, not a substitute for a complete essay with full paragraphs and developed analysis.
Downloadable Resources
Paragraph Structure Guide PDF - PEEL method reference.
Cause and Effect Essay Outline Block Structure Blank Template PDF - Fill in your causes and effects.
Cause and Effect Essay Outline Chain Structure Blank Template PDF - Map your causal chain.
Filled Templates
Block Structure Filled Outline PDF - Completed structure for reference.
Chain Structure Filled Outline PDF - Sequential format filled in.
All resources are immediately downloadable and customizable for your specific assignment.
WANT THE WHOLE THING DONE?
Don't Pay Until You're Impressed
- Our writers handle research through final draft
- Properly outlined and structured
- Unlimited revisions included
- Fast delivery, even last-minute orders
From outline to A-grade essay; we've got you.
Order Now-19320.jpg)


-19317.jpg)



